Condensed Phase#
Introduction
Intro paragraph
Notes
To Do
Think about coherent plan
Implement
Colaboration
Star formation is not my expertise so if you want to help, feel free to comment the contribution you could make
Introduction#
Water in the condensed phase#
» Phase diagram
The earth is the only planet of our solar system that can sustain water in it’s three physical states (solid, liquid, gas).
Liquid
supercooled liquid water
High density vs low density liquid
Scihub link - Structure and phase diagram of high-density water: The role of interstitial molecules - Molecular dynamics paper but interesting
Infrared Investigation
Note
IR Spectra of the different phases
Gas spectra
Absorption spectra of liquid and solid water
» Cluster
Water dimer
History Review
Model [Mukhopadhyay et al., 2018]
Influence on the IR bands
Cooperative Hydrogen Bonding
increase in dipole moment with the increase in hydrogen bonding coordination
Effect on the IR vibrations
Note
what these underlying absorption peaks represent?
Is it the number of H bonds that is important [Walrafen, 1972]
the Type of H bonds (single, bifurcated, trifurcated) ?
HB bending angle ? [Møller et al., 2004]
Nature of the formed or broken donor and acceptor hydrogen bonds [Millo et al., 2005]
length of the hydrogen bonds [Schmidt and Miki, 2007]
The absorption bands also reflect coherent vibrational transfer involving several to many water molecules - [Yang and Skinner, 2010] (liquid water work)
Fitting method
OH stretch is big potato, sum of multiple subfeature (peaks)
Gaussian or Lorentzian ?
Voight profile ? (combination of both)
Other clusters
» Crystalisation
At molecular scales (few molecules up to 100 ?) - Matrix isolation techniques
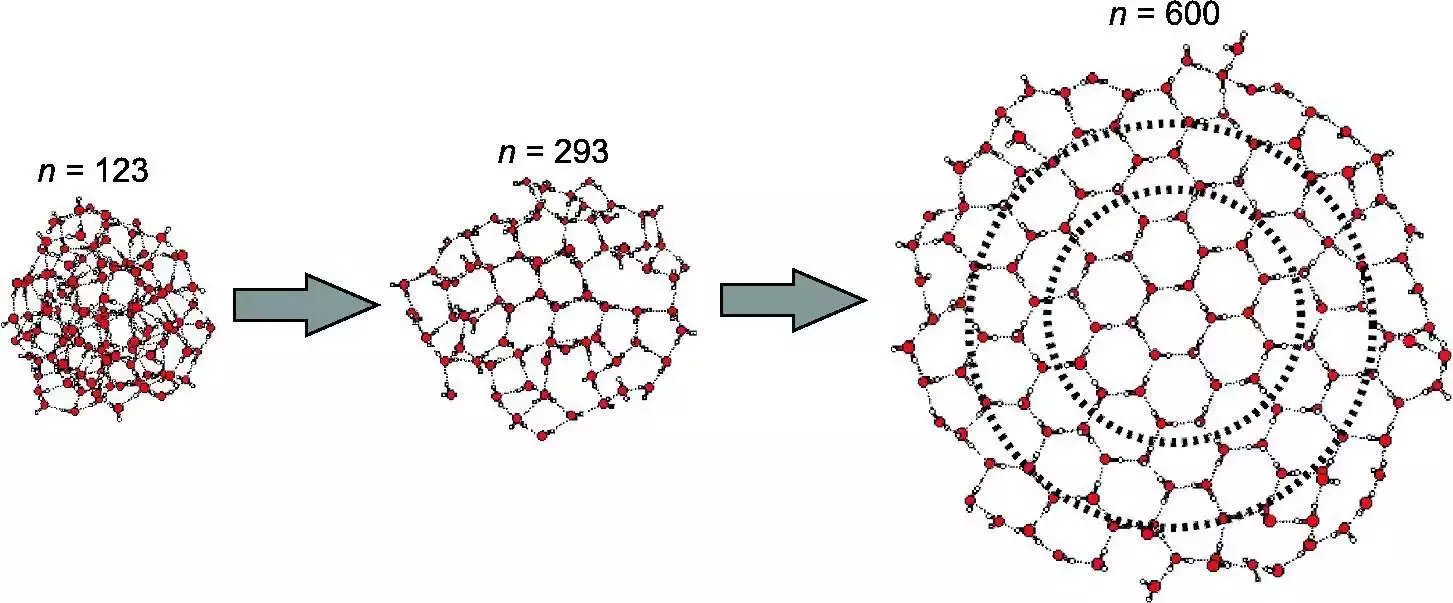
Question
At what number of molecule do you consider a solid phase
Liquid#
Review: [Malenkov, 2009]
Note
Good article to make the link between the 2 phases
Solid#
Glasses and supercooled liquids#
Review: [Lubchenko and Wolynes, 2007]