and Mixed#
Catchy Phrase
Amorphous ice, a sight to behold,
Molecules within, a story untold.
A symphony of atoms, dancing free,
In a frozen world, as far as the eye can see.
But cosmic rays and UV photons reign,
Their energy drives the molecules insane.
They dance and bond in a wild orgie,
Creating new compounds, with such intensity.
Carbon, oxygen, nitrogen too,
Reacting wildly, as if on cue.
Amino acids, sugars, and more,
All formed in ice, like never before.
This cosmic dance, a sight to see,
In the depths of space, so wild and free.
The energy of the cosmos, a driving force,
Creating new molecules, without remorse.
Amorphous ice, a laboratory,
Where cosmic rays and photons play with glee.
A mysterious world, beyond our sight,
Yet essential to life, both day and night.
– Vince (& ChatGPT)
Key Litterature:
- 1
- 2
Links
- 1
- 2
Astrochemistry#
Note
General introduction to Astrochemistry
» Molecules in the ISM
- table list of molecules in the ISM
TPD of ASW + hydrophobes []
» ASW + molecules
Ethane
Ethane properties:
- volatile
Where is ethane found in the solar system ?
- Ice on solar stem bodies but also one of the more commonly form of gas-phase hydrocarbons
- Pluto and other TNO’s
- Clouds of Titan (+ liquid phase)
- Cometary comae - mixing with ASW ?
Ethane Ice
[]: Ethane ices in the outer Solar System: Spectroscopy and chemistry
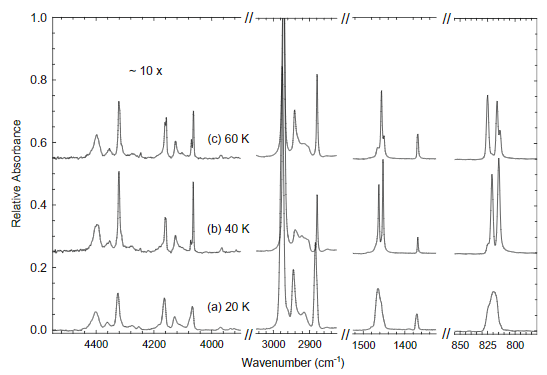
3 different solid phases:
- Amorphous: 20K
- Metastable: 40K
- Crystaline: 60K
Note
- Hudson assigned only two bands in the 3000 cm-1 region even though we can clearly see there is 3 (even a 4th tiny shoulder).
- Why ?
- Check on this later articles where optical constants are extracted.
[]: Infrared spectra and optical constants of astronomical ices: II. Ethane and ethylene
Note
- Are the assignment of bands the same ?
- If not, what does that say about the IR assignment litterature ?
Data is accessible Here for T of 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 K. Good to compare with our data. Are also given free software for:
- Optical Constants
- Interference Fringes
- Spectral Calculation
Ethane + water
- [] (Experimental method described in Dartois 2010, 2009, 2008)
Intro
Interaction of hydrocarbons with water ice at low temperatures could lead to the formation of clathrate hydrates (not to be confused with hydrates or ice mixture)
2 main crystalline clathrate hydrate cubic(?) structures:
- Type 1
- Type 2 For each structure, cage’s number ratio and filling ratio with guest moleculesinfluence the spectroscopic signature of the trapped molecules (ethane)
Note
How is the water spectra modified?
Some models do include clathrate hydrates in the evolution of solar system bodies:
- Combe 2019
- …
Note
Have a look later
- How is the water ice treated
- ethane:oxirane clathrate ([Richardson et al., 1985])
Method
- Form ice Ih layer (several micron thick)
- Pressurized the chamber with ethane gas (25 bars) for 15 days! - diffusion kinetics …
IR spectra steps of 20K
Results/Discussion
Pure ethane clathrate hydrate is exepected to be Type 1 (good agreement between [] and [Richardson et al., 1985]).
Main outcomes: formation of an ethane clathrate hydrate gives rise to a very unique band pattern, distinct from the observed features of the various ethane phases.
- Band splitting in fundamental μ7 degenerate mode region around 2970 cm-1
- …
Unique IR feature can be allocate to ethane clathrate hydrate Type 1.
But
When species are mixed they can induce formation of type 2 clathrate hydrates []
Note
- Ethane liquid density = 462.7 kg/m3 - Younglove 1987
Fig. 15 Explain: source Wikimedia#