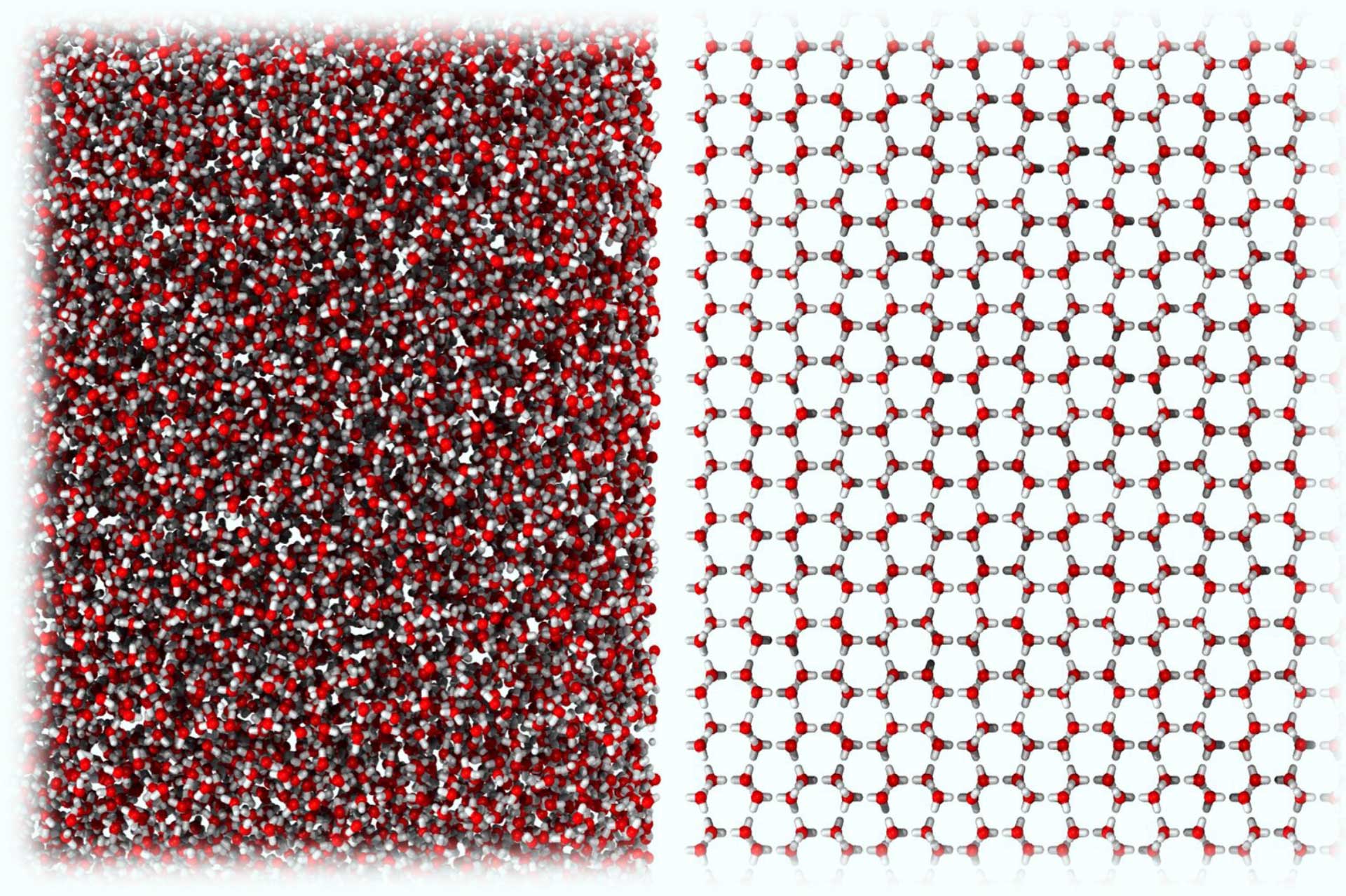
is Amorphous#
Catchy Phrase
Amorphous water ice, shapeless and still,
A formless beauty that seems to spill,
Over surfaces, with no defined shape,
A sight that’s unique and hard to escape.
It’s formed when water freezes fast,
And loses its structure in the cast,
Of cold and rapid freezing pace,
A sight that seems to hold its place.
It’s found on comets, asteroids, and more,
A form of water that’s hard to ignore,
A substance that’s elusive and rare,
A beauty that’s formed without a care.
It’s a sight to behold, with its misty form,
A beauty that seems to weather the storm,
Of time and space, and endless nights,
A thing of beauty, pure and bright.
So let us marvel at amorphous ice,
A substance formed in a flash, precise,
A wonder that’s hard to replicate,
A beauty that’s formed without a mistake.
– Vince (& ChatGPT)
Plan
Amorphous Ices#
Litterature#
Study Title Year “Infrared spectra of amorphous solid water” by G.A. Baratta and J.A. Westley 1989 “Infrared spectra of amorphous solid water: Implications for interstellar and cometary ice” by L.D. Deshmukh et al. 2004 “H2O ice in the interstellar medium: a comparison between observed and simulated infrared spectra” by C.A. Boogert et al. 2015 “Ice grain morphology and infrared spectra in protoplanetary disks” by M. Min et al. 2016 “The Low-Temperature Infrared Spectrum of Amorphous Solid Water: A Spectroscopic and Theoretical Study” by J. P. Lewis et al. 2000 “Mid-infrared spectroscopy of interstellar ice analogs” by J.M. Brown et al. 2007 “A laboratory study of the mid-infrared spectra of amorphous solid water and water-rich ices” by A.G.G.M. Tielens et al. 2008 “Spectroscopic properties of amorphous solid water: a review” by P. Ehrenfreund et al. 2015
Review#
- Review []
Bulk Organisation#
Definition#
Experiments#
- Variation of the deposition angle
Controlling the Morphology of Amorphous Solid Water
- Deposition temperature variations
- Annealing processes
Porosity#
[]
Definition#
- Controlling the
Experiments#
- Different types
Insert here table of different groups:
- NASA Ames: Mastrapa, Sandford
- Is data available, yes
Infrared Spectroscopy#
Key Papers:
- Mastrapa (2008, 2009)
- Jenny
What did we leran#
- ASW is porous
- 3 µm band is changing when the T is increased
- Water ice IR Band assignement taken from []
Warning
table was ther but got suppressed, to check
to cite:
- a [Bertie and Whalley, 1964]
- b [Hardin and rvey, 1973]
- c [Hudgins et al., 1993]
- d [Ockman, 1958]
- e [Whalley, 1977]
Note
- TO, LO, what does this mean ?
Insert own crystaline and amorphous spectra with different asssignments vertical bar
Link with Optical Constants
- Real and imaginary part (how do they relate to what we observe in space)
Differential Scanning Calorimetry#
tg at 136K (ramp 30K.min-1) –> Increase in heat capacity (lower than other amorphous solid: similar to SiO2 - GeO2) –> Imply limited number of entropically different configurational states in the fluid state following tg
Dielectric relaxation behaviour expected to be determined by two processes both involving a thermaly activated dipolar reorientation:
- translational-rotational diffusion of water molecules if the whole H-Bonded network relaxed within limitation of entropically different configurations
- rotational diffusion of water molecules within a fixed H-Bonded structure as breaches of the Bernal-Fowler rules. –> 2 kinds of Bjerrum defects
- Scattering
ASW at 140K - true glass or very viscous liquid ? What is the difference
Desorption#
[]